Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Determining Elliptic Distortion#
This example shows how to determine the elliptic distortion of an diffraction pattern from uncorrected 2-fold astigmatism. Determining the exact elliptic distortion is important for tasks such as
Orientation mapping
Angular Correlation (AC)
Fluctuation Electron Microscopy (FEM)
And many other 4-D STEM techniques
Note that this workflow might change (simplify and improve!) in the future as pyxem 1.0.0 is developed/released.
First, we import the necessary packages and make a single test diffraction pattern.
import pyxem.data.dummy_data.make_diffraction_test_data as mdtd
import pyxem as pxm
import pyxem.utils.ransac_ellipse_tools as ret
import hyperspy.api as hs
from skimage import morphology
from scipy.signal import convolve2d
from pyxem.signals.diffraction2d import Diffraction2D
import math
import numpy as np
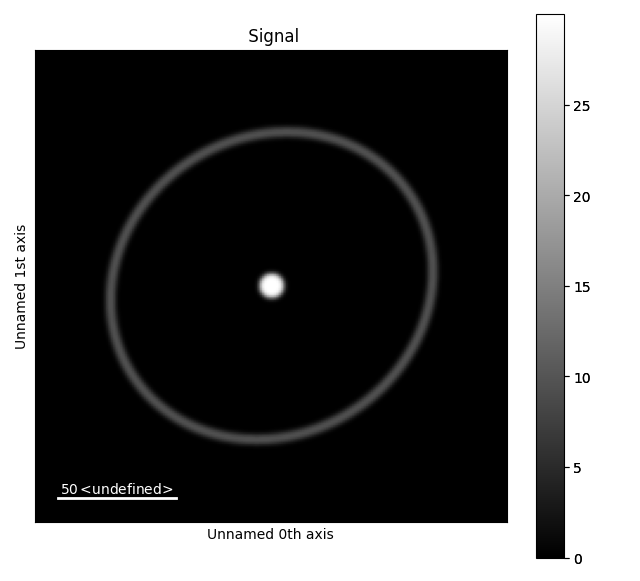
test_data = mdtd.MakeTestData(200, 200, default=False)
test_data.add_disk(x0=100, y0=100, r=5, intensity=30)
test_data.add_ring_ellipse(x0=100, y0=100, semi_len0=63, semi_len1=70, rotation=45)
s = test_data.signal
s.set_signal_type("electron_diffraction")
s.plot()
"""
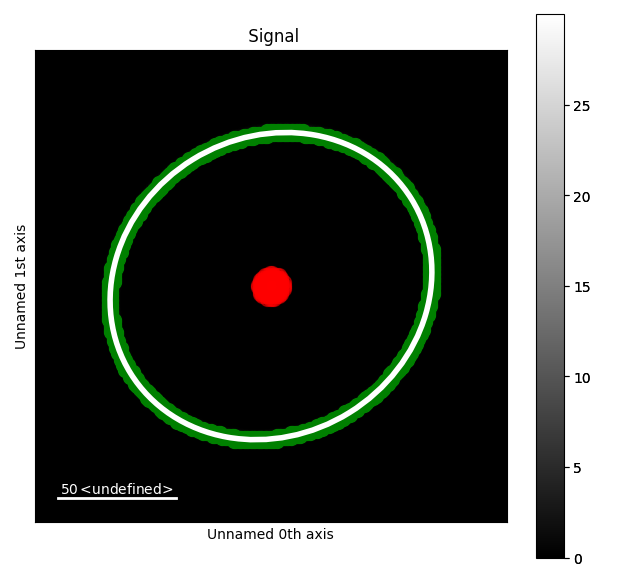
Using RANSAC Ellipse Determination
----------------------------------
The RANSAC algorithm is a robust method for fitting an ellipse to points with outliers. Here we
use it to determine the elliptic distortion of the diffraction pattern and exclude the zero
beam as "outliers". We can also manually exclude other points from the fit by using the
mask parameter.
"""
center, affine, params, pos, inlier = pxm.utils.ransac_ellipse_tools.determine_ellipse(
s, use_ransac=True, return_params=True
)
el, in_points, out_points = pxm.utils.ransac_ellipse_tools.ellipse_to_markers(
ellipse_array=params, points=pos, inlier=inlier
)
s.plot()
s.add_marker(in_points, plot_marker=True)
s.add_marker(el, plot_marker=True)
s.add_marker(out_points, plot_marker=True)
"""
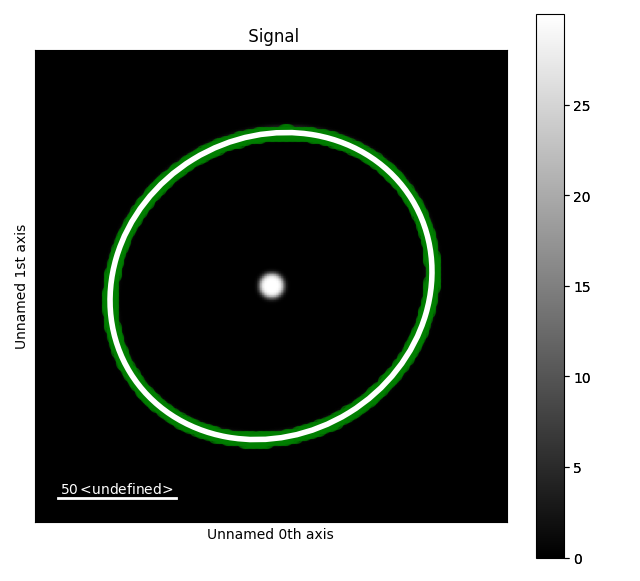
Using Manual Ellipse Determination
----------------------------------
Sometimes it is useful to force the ellipse to fit certain points. For example, here we
can force the ellipse to fit the first ring by masking the zero beam.
"""
mask = s.get_direct_beam_mask(radius=20)
center, affine, params, pos = pxm.utils.ransac_ellipse_tools.determine_ellipse(
s,
return_params=True,
mask=mask.data,
num_points=500,
use_ransac=False,
)
el, in_points = pxm.utils.ransac_ellipse_tools.ellipse_to_markers(
ellipse_array=params,
points=pos,
)
s.plot()
s.add_marker(in_points, plot_marker=True)
s.add_marker(el, plot_marker=True)
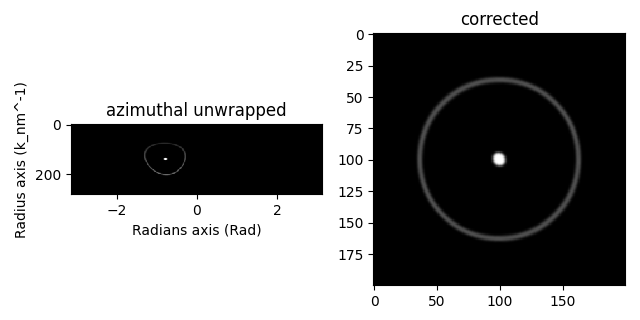
s.unit = "k_nm^-1"
s.beam_energy = 200
s.set_ai(affine=affine)
az = s.get_azimuthal_integral2d(npt=100, inplace=False)
corr = s.apply_affine_transformation(affine, inplace=False)
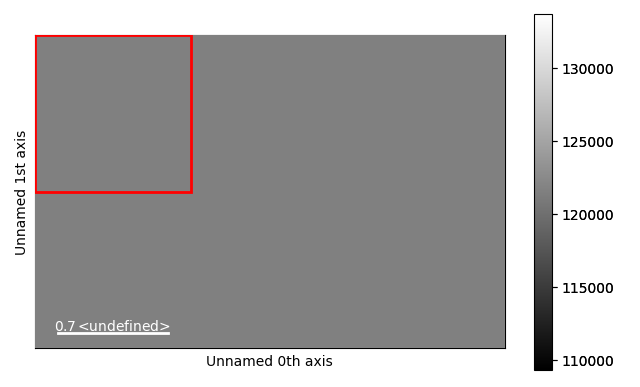
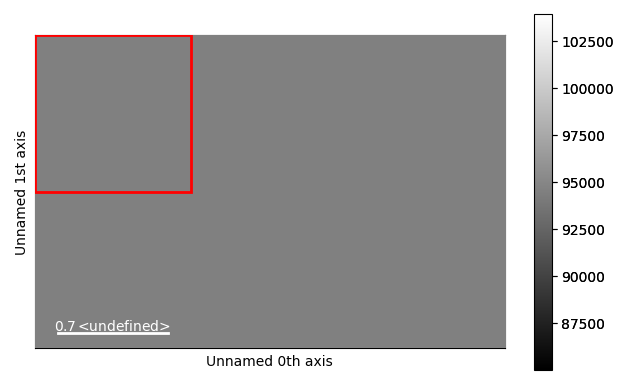
hs.plot.plot_images(
[az, corr],
label=["azimuthal unwrapped", "corrected"],
tight_layout=True,
colorbar=None,
)
/home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/pyxem/envs/latest/lib/python3.10/site-packages/pyxem/signals/diffraction2d.py:1782: VisibleDeprecationWarning: Function `set_ai()` is deprecated and will be removed in version 1.0.0. Use `pyxem.signals.diffraction2d.calibrate()` instead.
since="0.18",
/home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/pyxem/envs/latest/lib/python3.10/site-packages/pyxem/utils/pyfai_utils.py:145: VisibleDeprecationWarning: Function `_get_setup()` is deprecated and will be removed in version 1.0.0.
def _get_setup(wavelength, pyxem_unit, pixel_scale, radial_range=None):
/home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/pyxem/envs/latest/lib/python3.10/site-packages/pyxem/utils/pyfai_utils.py:32: VisibleDeprecationWarning: Function `get_azimuthal_integrator()` is deprecated and will be removed in version 1.0.0.
def get_azimuthal_integrator(
/home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/pyxem/envs/latest/lib/python3.10/site-packages/pyxem/utils/pyfai_utils.py:108: VisibleDeprecationWarning: Function `_get_displacements()` is deprecated and will be removed in version 1.0.0.
def _get_displacements(center, shape, affine):
[ ] | 0% Completed | 212.33 us
[########################################] | 100% Completed | 100.53 ms
[ ] | 0% Completed | 233.01 us
[########################################] | 100% Completed | 103.65 ms
[<Axes: title={'center': 'azimuthal unwrapped'}, xlabel='Radians axis (Rad)', ylabel='Radius axis (k_nm^-1)'>, <Axes: title={'center': 'corrected'}>]
"""
Ellipse from Points
-------------------
This workflow will likely change slightly in the future to add better parllelism,
but here is how to determine the ellipticity from a set of points.
"""
# making a test elliptical diffraction pattern
xf, yf, a, b, r, nt = 100, 115, 45, 35, 0, 15
data_points = ret.make_ellipse_data_points(xf, yf, a, b, r, nt)
image = np.zeros(shape=(200, 210), dtype=np.float32)
for x, y in data_points:
image[int(round(x)), int(round(y))] = 100
disk = morphology.disk(5, np.uint16)
image = convolve2d(image, disk, mode="same")
data = np.zeros((2, 3, 210, 200), dtype=np.float32)
data[:, :] = image.T
s = Diffraction2D(data)
# Finding the peaks
s_t = s.template_match_disk(disk_r=5)
peak_array = s_t.find_peaks(
method="difference_of_gaussian",
threshold=0.1,
lazy_output=False,
interactive=False,
).data
c = math.sqrt(math.pow(a, 2) - math.pow(b, 2))
xc, yc = xf - c * math.cos(r), yf - c * math.sin(r)
ellipse_array, inlier_array = ret.get_ellipse_model_ransac(
peak_array,
yf=yf, # center y
xf=xf, # center x
rf_lim=15, # max center error
semi_len_min=min(a, b) - 5, # min semi-len
semi_len_max=max(a, b) + 5, # max semi-len
semi_len_ratio_lim=2, # max semi-len ratio
max_trials=50,
min_samples=10, # min inliers to fit
)
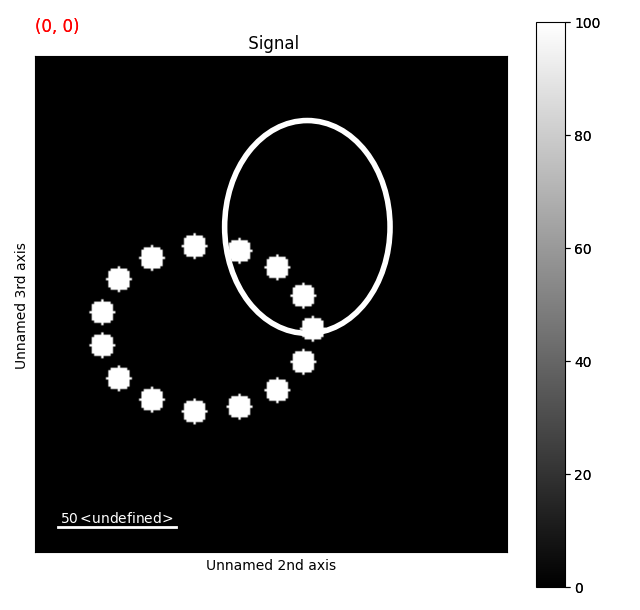
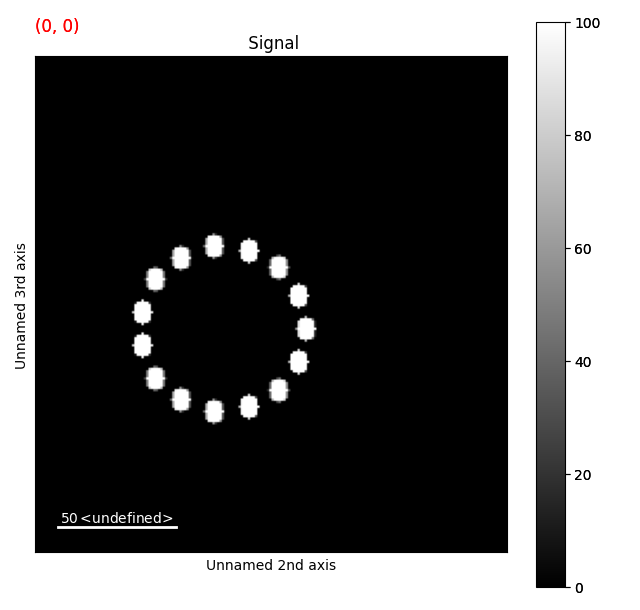
s.add_ellipse_array_as_markers(ellipse_array)
el = ellipse_array[0, 0]
affine = ret._ellipse_to_affine(el[2], el[3], el[4])
tr = s.apply_affine_transformation(affine, inplace=False)
tr.plot()
[ ] | 0% Completed | 144.27 us
[########################################] | 100% Completed | 100.52 ms
[ ] | 0% Completed | 127.44 us
[ ] | 0% Completed | 100.40 ms
[ ] | 0% Completed | 200.75 ms
[ ] | 0% Completed | 301.10 ms
[ ] | 0% Completed | 401.45 ms
[ ] | 0% Completed | 501.84 ms
[########################################] | 100% Completed | 602.22 ms
0%| | 0/6 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
100%|██████████| 6/6 [00:00<00:00, 125.42it/s]
[ ] | 0% Completed | 305.45 us
[########################################] | 100% Completed | 101.04 ms
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 18.800 seconds)